
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of bringing eggs and sperm into contact in the laboratory. The goal: to facilitate and achieve fertilization.
The resulting embryo(s) are cultured in the laboratory and then transferred to the uterus or frozen for a future transfer.
This technique is indicated for couples with some type of infertility, whether female or male, such as:
To increase the chance of success, controlled ovarian stimulation is performed with hormonal treatment (gonadotropins), for 9-12 days. This allows the growth of several follicles and therefore, the obtaining of several eggs.
The gynaecologist adapts the stimulation protocol for each patient and during ovarian stimulation, performs ultrasound and hormonal monitoring tests.
When the follicles have reached the ideal size, an HCG injection is administered that allows the final maturation of the eggs and the ovarian puncture is programmed at 34-36 hours later.
The ovarian puncture is the procedure indicated to recover the eggs, through the aspiration of the follicular fluid.
It is a process that is carried out in the operating room under sedation, it is painless, lasts between 15-20 minutes and does not require admission.
During the puncture, the gynaecologist accesses the ovaries via transvaginal with the help of an ultrasound transducer. The follicular liquids that are extracted are transferred to the embryology laboratory.
On the same day of the ovarian puncture, the sperm sample is prepared in the laboratory, which may be from the couple or a donor. If it belongs to the couple, the sample must be obtained with an abstinence of between 2-7 days.
In the laboratory, the sperm sample is processed to select the spermatozoa with the best quality and mobility. There are different techniques to carry out this process and each one will be indicated according to the initial quality of the sample.
Mature oocytes are inseminated a few hours later (4-6 hours post-puncture), using the most suitable technique:
In Vitro Fertilization
Mature eggs are placed with sperm so fertilization can occur naturally. This is used when the semen quality is good and there is no previous cycle with a fertilization failure.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
One sperm is injected directly into the egg using micromanipulation techniques. The eggs must first be stripped of surrounding cells.
Specific TechniquesIntracytoplasmic Morphologically Selected Sperm Injection (IMSI)
IMSI is an advanced version of ICSI where sperm are selected in real-time using a high-magnification microscope (around 6,000x).
Specific TechniquesBetween 16 and 20 hours after insemination, fertilized eggs (zygotes) are identified and evaluated. The presence of two pronuclei (one female and one male) confirms correct fertilization.
Eggs that failed to fertilize or fertilized abnormally are discarded at this point.
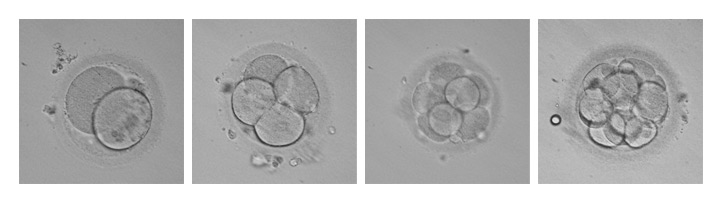
The embryos are cultured in a time-lapse incubator for 2–6 days depending on the case, in stable conditions of temperature, pH and gases.
During this time, embryologists evaluate embryo development, according to morphological criteria and cell division patterns, with the aim of selecting the best embryos for embryo transfer or freezing.
Embryo transfer involves placing embryos into the uterine cavity, using a catheter. It is carried out between day 3 and 6 of embryo cultivation, depending on each case.
It is a process that is carried out in a room attached to the laboratory, it is simple, painless, does not require sedation and lasts approximately 5-10 minutes. Once the transfer is completed, the patient must remain at rest for a few minutes.
Fresh Transfer
It consists of transfer the embryo(s) in the same cycle in which the ovarian puncture has been carried out, without previously freezing. It is usually performed between day 3 and 6 of embryo cultivation and the leftover embryos are frozen.
Forzen-Thawing Embryotransfer
It is the transfer of a previously vitrified embryo or embryo from an earlier IVF cycle.
The embryos are cryopreserved in the GIROFIV Embryo Bank, until the couple wants to undergo a new transfer or end the freezing.
The patient will be able to know if she is pregnant, through a blood test of the hormone beta hCG, between 12 and 13 days after the transfer.